#include <ACDCTerminal.h>
Public Attributes | |
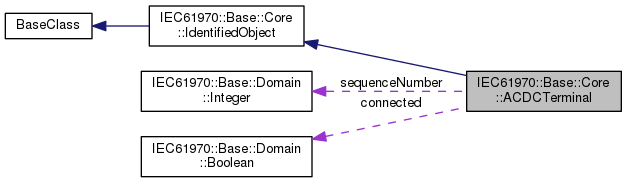
| IEC61970::Base::Domain::Boolean | connected |
| IEC61970::Base::Domain::Integer | sequenceNumber |
 Public Attributes inherited from IEC61970::Base::Core::IdentifiedObject Public Attributes inherited from IEC61970::Base::Core::IdentifiedObject | |
| IEC61970::Base::Domain::String | aliasName |
| IEC61970::Base::Domain::String | description |
| IEC61970::Base::Domain::String | mRID |
| IEC61970::Base::Domain::String | name |
| std::list< IEC61970::Base::DiagramLayout::DiagramObject * > | DiagramObjects |
An electrical connection point (AC or DC) to a piece of conducting equipment. Terminals are connected at physical connection points called connectivity nodes.
| IEC61970::Base::Domain::Boolean IEC61970::Base::Core::ACDCTerminal::connected |
The connected status is related to a bus-branch model and the topological node to terminal relation. True implies the terminal is connected to the related topological node and false implies it is not. In a bus-branch model, the connected status is used to tell if equipment is disconnected without having to change the connectivity described by the topological node to terminal relation. A valid case is that conducting equipment can be connected in one end and open in the other. In particular for an AC line segment, where the reactive line charging can be significant, this is a relevant case.
| IEC61970::Base::Domain::Integer IEC61970::Base::Core::ACDCTerminal::sequenceNumber |
The orientation of the terminal connections for a multiple terminal conducting equipment. The sequence numbering starts with 1 and additional terminals should follow in increasing order. The first terminal is the "starting point" for a two terminal branch.
 1.8.13
1.8.13